
The citric acid cycle is "thought by many experts to be among the most ancient of biological processes," study co-author George Cooper, a chemist at NASA Ames Research Center, told. In a different study, researchers discovered molecules that make up key parts of a vital biological pathway, the citric acid cycle, in a number of carbonaceous chondrites. "Are these building blocks of life transferred to other places where they might be useful? Can alternative building blocks be used to build other things?" "All this has implications for the origins of life on Earth and potentially elsewhere," Callahan said. "At the start of this project, it looked like the nucleobases in these meteorites were terrestrial contamination - these results were a very big surprise for me," study co-author Michael Callahan, an analytical chemist and astrobiologist at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, told. "Finding nucleobase compounds not typically found in Earth's biochemistry strongly supports an extraterrestrial origin," Cleaves said. Intriguingly, three of these nucleobase analogs are very rare in Earth biology, and were not found in soil and ice samples from the areas near where the meteorites were collected at the parts-per-billion limits of their detection techniques. Two of the carbonaceous chondrites contained a diverse array of nucleobases and structurally similar compounds known as nucleobase analogs. The analytical techniques probed the mass and other features of the molecules to identify the presence of extraterrestrial nucleobases and see that they apparently did not come from the surrounding area. This was the first time all but two of these meteorites had been analyzed for nucleobases. To help confirm if any nucleobases seen in meteorites were of extraterrestrial origin, scientists used the latest scientific analysis techniques on samples from a dozen meteorites - 11 organic-rich meteorites called carbonaceous chondrites and one ureilite, a very rare type of meteorite with a different chemical composition. "People have been finding nucleobases in meteorites for about 50 years now, and have been trying to figure out if they are of biological origin or not," study co-author Jim Cleaves, a chemist at the Carnegie Institution of Washington, told.

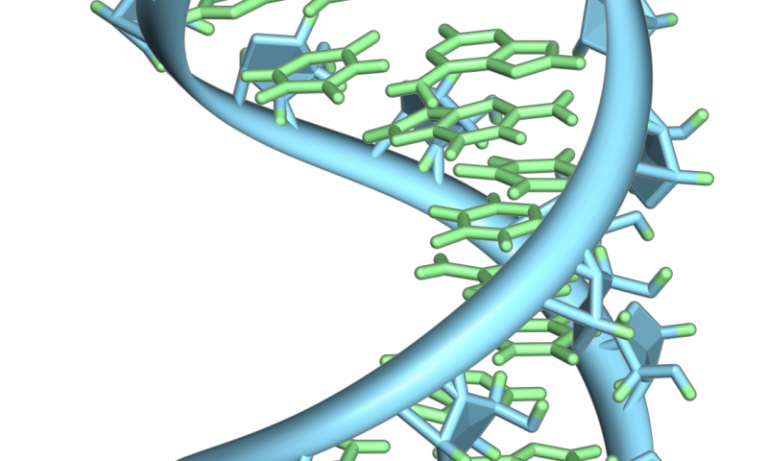
However, it has been very difficult to prove that these molecules are not contamination from sources on Earth. Investigators have also found nucleobases, key ingredients of DNA, in meteorites before. Space rocks just like these may have been a vital source of the organic compounds that gave rise to life on Earth. The DNA has a net negative charge and moves from the negative electrode toward the positive electrode.Past research had revealed a range of building blocks of life in meteorites, such as the amino acids that make up proteins. Once the gel has solidified, the DNA is loaded on the gel and electric current is applied. After cooling, the gel solution is poured into a casting tray. Agarose powder is added to a buffer and heated. Usually the gel is made of a chemical called agarose. Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate DNA fragments of different sizes. Learn more by selecting the Sequencing at Speed animation here. Sanger’s genome sequencing has led to a race to sequence human genomes at a rapid speed and low cost, often referred to as the $1000 in one day sequence. For his work on DNA sequencing, Sanger received a Nobel Prize in chemistry in 1980. The sequence is read from a laser scanner. Even a difference in length of a single base can be detected. After the reaction is over, electrophoresis is performed. Chain elongation continues until a fluorescent dideoxy nucleotide is incorporated, after which no further elongation takes place. For detection purposes, each of the four dideoxynucleotides carries a different fluorescent label. The tubes are labeled as A, T, G, and C according to the ddNTP added. In addition to each of the four tubes, limited quantities of one of the four dideoxynucleotides are added to each tube respectively.

The DNA is divided into four tubes in which a primer, DNA polymerase, and all four nucleotides (A, T, G, and C) are added. The DNA sample to be sequenced is denatured or separated into two strands by heating it to high temperatures. The DNA sequence readout is shown on an electropherogram that is generated by a laser scanner.
The DNA is separated by capillary electrophoresis on the basis of size, and from the order of fragments formed, the DNA sequence can be read. \): In Frederick Sanger's dideoxy chain termination method, dye-labeled dideoxynucleotides are used to generate DNA fragments that terminate at different points.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
